If you are looking for what is Extended Reality. You are in the right place. In recent years, technology has made significant strides, revolutionizing the way we perceive and interact with the world around us. One such breakthrough is the advent of Extended Reality (XR), an umbrella term encompassing various immersive technologies that blend the physical and virtual realms.
Read carefully What Is Extended Reality. XR extends beyond the boundaries of traditional virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), combining them with mixed reality (MR) to create a seamless and interactive experience. In this article, we delve into the exciting world of XR and explore its transformative impact across industries and everyday life.
Understanding Extended Reality
Extended Reality (XR) represents a remarkable leap forward in the realm of immersive technologies, blurring the lines between the real and virtual worlds. It encompasses a spectrum of cutting-edge technologies that enable users to interact with digital content while simultaneously engaging with their physical surroundings. At its core, XR is a convergence of three key immersive technologies: virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR). Each of these components brings a unique set of capabilities and experiences to the table.
Virtual reality is perhaps the most well-known facet of XR. It transports users to entirely simulated environments, completely replacing the real world with a digitally constructed one. Through the use of specialized headsets and controllers, users are immersed in a virtual realm where they can explore, interact, and experience a wide range of scenarios, from traversing fantastical landscapes to engaging in thrilling gaming experiences. The goal of virtual reality is to create a sense of total presence, where users feel as though they have truly entered a different reality.
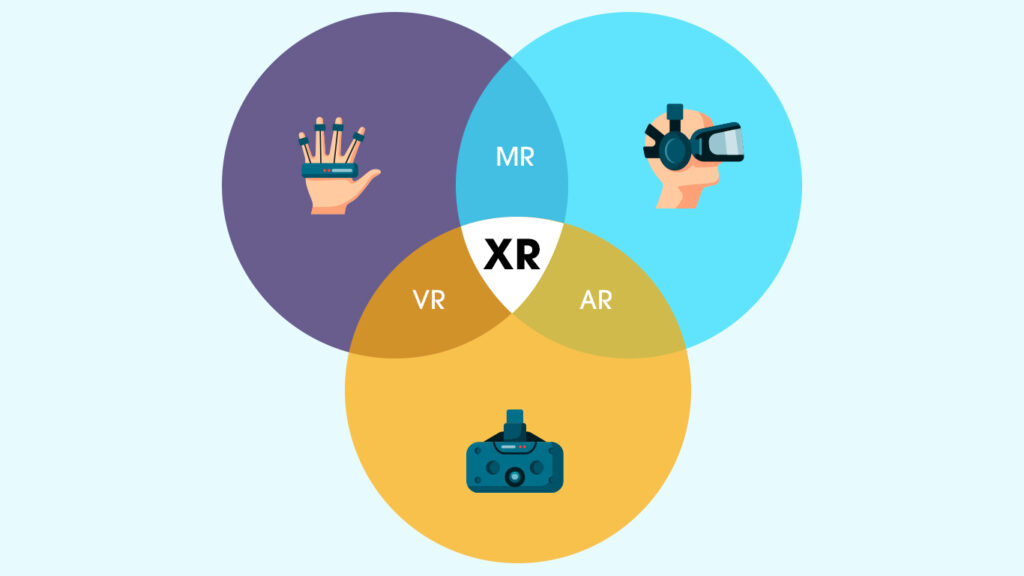
In contrast, augmented reality enhances our perception of reality by overlaying digital content onto the physical world. AR technology typically utilizes devices such as smartphones or smart glasses, which employ cameras and sensors to capture the user’s environment. Through advanced computer vision and image recognition algorithms, digital elements such as graphics, text, or 3D models are seamlessly superimposed onto the real-world view. This integration of virtual and real-world elements allows users to interact with and manipulate virtual objects while still maintaining a connection to their physical surroundings. AR has found widespread applications in areas like gaming, education, retail, and industrial sectors.
Mixed reality takes the concept of augmented reality a step further by seamlessly blending virtual and physical elements to create a cohesive and interactive environment. MR enables digital objects to interact with the real world in real-time, allowing users to experience the integration of both realms in a natural and intuitive manner. Unlike AR, where virtual content is superimposed onto the physical world, MR goes beyond mere overlays. It enables virtual objects to respond to physical elements and vice versa, creating a sense of true spatial and contextual awareness. Mixed reality has immense potential across various domains, from design and engineering to training and collaboration.
By combining the strengths of virtual reality, augmented reality, and mixed reality, Extended Reality opens up a world of possibilities for both individuals and industries. Users can immerse themselves in virtual environments, augment their perception of reality with digital overlays, or seamlessly integrate virtual and physical elements for truly interactive experiences. XR has the potential to transform how we learn, work, play, and connect with others, pushing the boundaries of what we thought was possible in the realm of human-computer interaction.
In summary, Extended Reality represents the convergence of virtual reality, augmented reality, and mixed reality, enabling users to engage with digital content while interacting with their physical surroundings. It offers a range of immersive experiences, from fully simulated virtual environments to digitally enhanced real-world interactions. As XR technology continues to evolve and improve, it holds the promise of reshaping industries, transforming education and training, enhancing entertainment experiences, and fundamentally changing the way we perceive and interact with the world around us.
Applications of Extended Reality

The impact of Extended Reality (XR) on the entertainment and gaming industries cannot be overstated. XR has ushered in a new era of immersive experiences that have revolutionized the way we engage with entertainment content and interact with gaming environments.
Virtual reality gaming stands at the forefront of XR’s influence on the entertainment landscape. With VR, players can step into entirely simulated worlds and become fully immersed in the experience. By donning a VR headset and utilizing motion controllers, users are transported to virtual realms where they can explore breathtaking landscapes, engage in heart-pounding adventures, and interact with virtual characters and objects. The sense of presence and immersion in VR gaming is unparalleled, creating an intense level of engagement and a profound feeling of actually being inside the game.
Augmented reality has also made significant strides in the entertainment industry. AR-based mobile games, such as Pokémon Go, have taken the world by storm, blurring the boundaries between the virtual and physical realms. These games utilize the real-world environment as a canvas, overlaying digital content onto the user’s surroundings. Players are encouraged to explore their surroundings, discovering virtual creatures, objects, or points of interest and engaging in gameplay within their own neighborhoods, parks, or cities. AR gaming brings a sense of magic and discovery to everyday life, fostering an interactive and social gaming experience.
Extended Reality has also unlocked new possibilities for interactive storytelling. XR experiences allow users to become active participants in narratives, breaking the traditional passive consumption of media. In VR, users can step into the shoes of characters, experiencing stories from their perspective and making choices that shape the outcome. This interactive storytelling format enables a deeper emotional connection and a more personalized experience for the audience. Additionally, AR-based storytelling experiences bring characters and objects into the real world, merging fiction with reality and creating memorable and engaging encounters.
The fusion of XR and entertainment has extended beyond gaming and storytelling. XR technologies have enabled immersive live performances, allowing audiences to experience concerts, theater, and events from the comfort of their homes through VR or AR platforms. Virtual reality concerts bring fans closer to their favorite artists, transporting them to virtual arenas where they can enjoy live performances and even interact with other virtual attendees. XR has also found applications in theme parks and attractions, enhancing visitors’ experiences with immersive and interactive elements.
The entertainment and gaming industries are continuously pushing the boundaries of XR technology, exploring new ways to captivate audiences and deliver unforgettable experiences. As XR hardware becomes more accessible and content creators embrace the potential of this medium, we can anticipate even more groundbreaking developments in the future. Extended Reality has transformed entertainment and gaming into truly immersive and participatory experiences, offering users a gateway to new dimensions of engagement and enjoyment.
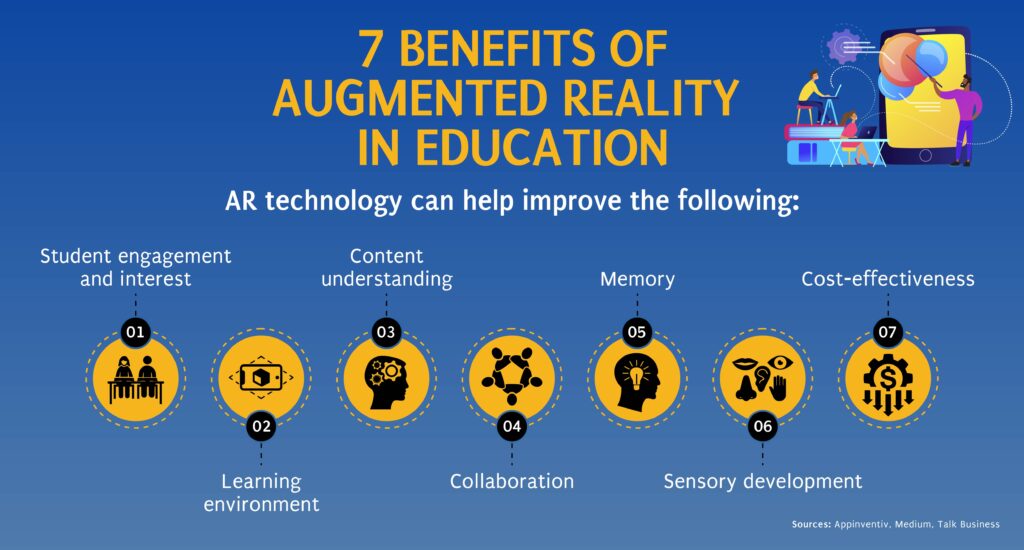
Extended Reality (XR) has emerged as a game-changer in the field of education and training, offering innovative and immersive learning experiences that go beyond traditional methods. By leveraging XR technologies, such as virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), education and training can be transformed into interactive and engaging journeys.
Virtual reality simulations have proven to be particularly powerful tools in education. VR enables students to step into historical events, bringing history to life in a way that textbooks or videos cannot match. They can explore ancient civilizations, witness pivotal moments in history, and gain a deeper understanding of the past by virtually immersing themselves in these environments.
Scientific phenomena that are difficult to visualize or recreate in a traditional classroom setting can be experienced firsthand through VR. Students can venture inside a human cell, explore the solar system, or witness the inner workings of complex scientific processes, making learning more tangible and engaging.
Furthermore, VR simulations provide a safe and controlled environment for students to practice and hone their skills. In fields such as medicine, engineering, or aviation, VR can offer realistic training scenarios without the need for expensive equipment or putting individuals at risk. Medical students, for instance, can perform virtual surgeries, allowing them to gain practical experience and refine their techniques before working with real patients. This hands-on approach in a risk-free environment fosters confidence and competence among learners.
Augmented reality has also made significant strides in enhancing education and training. AR overlays digital content onto the real world, enriching traditional textbooks and static learning materials. Textbooks can come alive with interactive 3D models, videos, and additional information, offering a more dynamic and engaging learning experience. For example, students studying biology can use AR to examine detailed 3D models of organs or organisms, rotating and dissecting them virtually for a better understanding. Complex concepts can be simplified and visualized, improving comprehension and retention.
AR also facilitates real-time information and guidance. Through AR-enabled devices, students can access supplementary information, translations, or explanations by simply pointing their device at a specific object or text. This immediate access to contextual information enhances the learning process, providing instant feedback and expanding the depth of knowledge available to learners.
XR technology in education and training fosters active participation and learner-centered experiences. It promotes critical thinking, problem-solving, and collaboration among students. By immersing themselves in virtual or augmented environments, learners become active participants rather than passive recipients of information. This hands-on and interactive approach enhances engagement, motivation, and knowledge retention.
Moreover, XR allows for personalized and adaptive learning experiences. With the ability to track and analyze user interactions, XR platforms can adapt content to individual learner needs, providing tailored guidance and challenges. This personalized learning approach caters to different learning styles and paces, ensuring that each student receives the support and resources they require.
In conclusion, XR has revolutionized education and training by providing immersive and interactive learning experiences. Through virtual reality simulations, students can explore historical events, delve into scientific phenomena, and practice complex procedures in a safe and controlled environment. Augmented reality overlays interactive content onto traditional learning materials, making education more engaging and accessible. As XR technology continues to advance, we can expect even more transformative applications in education, empowering learners and educators alike with innovative tools for enhanced knowledge acquisition and skill development.
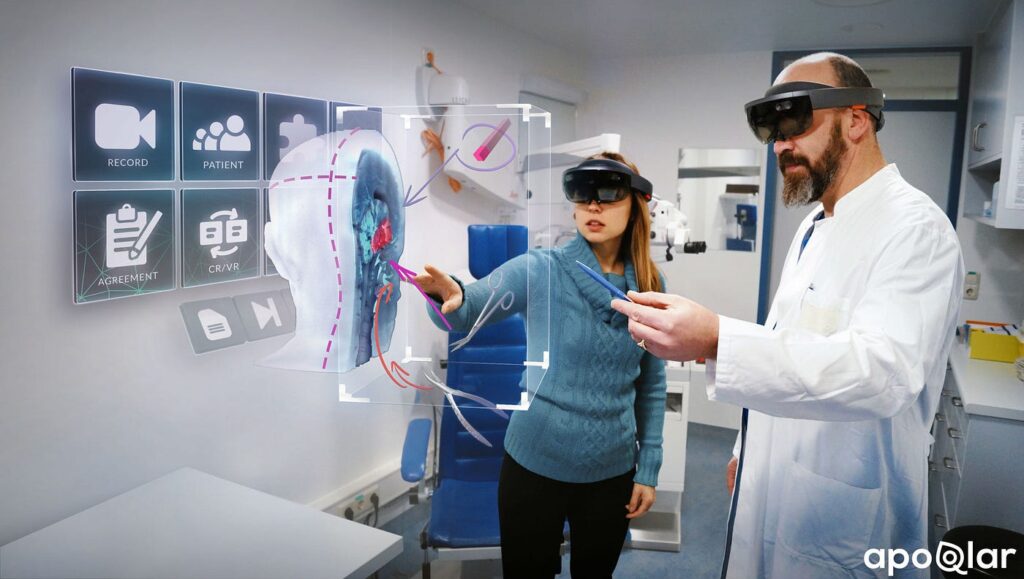

Extended Reality (XR) has emerged as a transformative force in the healthcare and medical fields, revolutionizing the way procedures are planned, medical education is conducted, and therapeutic interventions are implemented. By harnessing XR technologies such as virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), healthcare professionals are equipped with powerful tools to enhance patient care and improve outcomes.
One of the significant applications of XR in healthcare is in surgical planning and visualization. Surgeons can utilize VR to create highly detailed and accurate 3D models of patients’ anatomy from medical imaging data. These virtual models enable surgeons to explore and interact with the patient’s anatomy before stepping into the operating room, allowing for better planning and precision. Surgeons can practice complex procedures, assess potential risks, and identify optimal surgical approaches, leading to improved patient safety and surgical outcomes. VR simulations also offer a platform for collaborative decision-making among multidisciplinary teams, fostering communication and reducing errors.
Medical education benefits greatly from the integration of AR into traditional teaching methods. AR enables students and trainees to study anatomical structures and physiological processes in a dynamic and interactive manner. By overlaying 3D models of organs, systems, or diseases onto physical specimens or patient examinations, AR enhances the understanding of complex concepts. Students can visualize anatomical structures from different angles, explore variations, and gain a deeper comprehension of the human body. AR also allows for the integration of diagnostic information, such as lab results or medical imaging, directly onto patient examinations, facilitating real-time analysis and interpretation.
XR technology has therapeutic applications as well, improving patient experiences and aiding in rehabilitation. Virtual reality can be used as a distraction technique during painful procedures or to alleviate anxiety and discomfort. By immersing patients in virtual environments, VR distracts their attention from the procedure, reducing pain perception and stress levels. Additionally, VR simulations can assist in rehabilitation exercises by providing interactive and engaging environments for patients to practice physical movements, balance, or motor skills. These virtual rehabilitation programs can be personalized and adjusted to the specific needs of each patient, enhancing motivation and outcomes.
Moreover, XR enables remote healthcare delivery and telemedicine. With the help of XR devices, healthcare providers can conduct virtual consultations, remote monitoring, and even perform surgeries from a distance. This technology bridges geographical barriers, improving access to specialized care, particularly in rural or underserved areas. Patients can receive expert opinions and guidance without the need for physical travel, promoting convenience and efficiency in healthcare delivery.
While XR holds great promise in healthcare, challenges such as data privacy, regulatory compliance, and integration into existing workflows need to be addressed. Nevertheless, the transformative implications of XR in healthcare are undeniable, with the potential to revolutionize surgical planning, medical education, and therapeutic interventions. As technology continues to advance and accessibility improves, XR will continue to play a vital role in shaping the future of healthcare, enhancing patient care, and pushing the boundaries of medical innovation.

Extended Reality (XR) has emerged as a transformative tool in the field of architecture and design, revolutionizing the way professionals create, present, and experience their work. Through the integration of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), XR is reshaping the design process, enhancing communication with clients, and offering innovative ways to visualize and refine architectural and interior design concepts.
Virtual reality has had a profound impact on architectural visualization and client communication. With VR, architects and designers can create immersive and realistic virtual environments that allow clients to experience proposed designs as if they were physically present. By donning a VR headset, clients can explore virtual buildings, walk through spaces, and get a true sense of scale, proportion, and spatial relationships. This immersive experience helps clients to better understand the design intent and make informed decisions before the construction phase. VR can significantly reduce misunderstandings and miscommunications, leading to a more efficient and cost-effective design process.
Additionally, VR enables architects and designers to conduct virtual design reviews and collaborative sessions. Multiple stakeholders can simultaneously enter the virtual environment, allowing for real-time discussions, feedback, and revisions. This collaborative approach streamlines decision-making and fosters better teamwork among architects, clients, and other project participants. VR also facilitates the exploration of design alternatives by rapidly iterating and visualizing different concepts, ultimately leading to more innovative and refined designs.
Augmented reality is making significant strides in interior design, enhancing the visualization and customization of spaces. AR allows designers to overlay virtual furniture, fixtures, and decorations onto physical environments, providing clients with a clear understanding of how the final design will look and feel. By utilizing AR-enabled devices such as smartphones or tablets, users can place and manipulate virtual objects in real-time, allowing for instant visual feedback. This technology empowers clients to make informed decisions about interior design choices, such as furniture placement, color schemes, and finishes, before any physical changes are made. AR enables a more efficient design process by reducing the need for costly and time-consuming mock-ups or physical samples.
Moreover, AR can enhance the design and construction process by overlaying digital information onto the physical site. Architects and contractors can use AR to visualize building information models (BIM) and construction plans on-site, providing real-time guidance and information. This technology improves accuracy, reduces errors, and enhances the coordination between design and construction teams. AR can also aid in facility management by overlaying maintenance or repair information onto physical equipment or structures, facilitating quick and efficient maintenance operations.
As XR technology continues to advance, its integration into the architectural and design fields is becoming more seamless and accessible. The ability to create immersive VR experiences and overlay virtual content onto the real world through AR is transforming how designs are conceptualized, presented, and experienced. XR is enhancing collaboration, improving client engagement, and pushing the boundaries of creativity in architecture and design. With XR, architects and designers have powerful tools at their disposal to create remarkable and impactful designs, revolutionizing the way we interact with the built environment.
Challenges and Future Perspectives

While Extended Reality (XR) offers numerous benefits, it also faces certain challenges that need to be addressed for a more seamless and widespread adoption.
One of the primary challenges of XR is the technical limitations associated with the hardware and software components. Processing power is crucial for delivering immersive and realistic experiences, and advancements in hardware, such as more powerful GPUs and CPUs, are necessary to meet the demands of complex XR applications. Field of view (FOV) is another area that requires improvement.
Expanding the FOV can enhance immersion by allowing users to have a wider and more encompassing view of the virtual or augmented environment. Similarly, tracking accuracy plays a vital role in maintaining the illusion of presence and interaction within XR experiences. Advancements in tracking technologies, such as inside-out tracking or improved motion sensors, can contribute to a more accurate and responsive XR experience.
Accessibility and affordability are additional barriers to the widespread adoption of XR. Currently, high-quality XR devices can be costly, limiting their accessibility to a wider audience. However, as technology advances and economies of scale come into play, the cost of XR hardware is likely to decrease, making it more accessible to individuals, businesses, and educational institutions. Furthermore, efforts are being made to develop more user-friendly interfaces and intuitive interaction methods to enhance accessibility and ease of use for XR applications.
Looking ahead, the future of XR is promising. Advancements in technology will lead to enhanced visual fidelity, offering more realistic and immersive experiences. Higher display resolutions, improved rendering techniques, and better color reproduction will contribute to more visually stunning XR environments. Haptic feedback, which provides users with a sense of touch and interaction, will continue to improve, allowing for more realistic tactile experiences within XR. This advancement in haptic technology will enable users to feel the texture, weight, and resistance of virtual objects, further enhancing immersion.

Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) will amplify XR’s potential. AI algorithms can enhance object recognition, scene understanding, and natural language processing, making XR experiences more intelligent and responsive. ML algorithms can learn from user interactions and adapt XR environments to individual preferences, creating personalized and adaptive experiences.
The growth of 5G networks will play a significant role in the future of XR. With faster data transmission and lower latency, 5G will enable real-time interactions and seamless streaming of XR content. This will enhance collaborative XR experiences, remote training, and real-time communication in virtual environments.
In conclusion, while Extended Reality faces challenges related to technical limitations, accessibility, and affordability, the future of XR is promising. As technology continues to advance, we can expect improved hardware capabilities, enhanced visual fidelity, more realistic haptic feedback, and increased interactivity. The integration of AI and ML will further enhance XR experiences, making them more intelligent and adaptive. With the growth of 5G networks, XR will become more seamless and interactive, paving the way for exciting applications in various fields, including entertainment, education, healthcare, and design.
Conclusion
Extended Reality is a transformative technology that bridges the gap between the physical and digital worlds. Its applications span across various sectors, offering immersive experiences and enhancing productivity, education, healthcare, and entertainment. While challenges persist, ongoing technological advancements and increasing accessibility indicate a bright future for XR. As we continue to push the boundaries of Extended Reality, we can expect a new era of interaction and engagement that will reshape our perception of reality.
Extended Reality is not just a buzzword but a powerful tool that has the potential to reshape industries and revolutionize our daily lives. As we embark on this XR journey, we must embrace the possibilities it offers and strive to leverage its full potential for a better, more immersive future.
I hope you guys find the answer to what is extended reality technology. Thank you for Reading our article. Don’t forget to click the like on our Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and Pinterest. Your support means a lot to us. All social media links are found on the very down of this page.
I hope you like our article about what is Extended Reality.
Feel free to comment more down below your idea and don’t hesitate to share or pin our article…
Related Articles-
Ceylebrity News And Blog- WWW.CEYLEBRITYNEWS.COM
Visit Our Online Shopping Website- WWW.CEYLEBRITY.COM
Ceylebrity Sinhala News And Articles- WWW.CEYLEBRITYNEWS.LK
Share.......




15 thoughts on “What Is Extended Reality (XR)? Everything You Need To Know 2024”